California Wildfires Create Their Own Weather Patterns
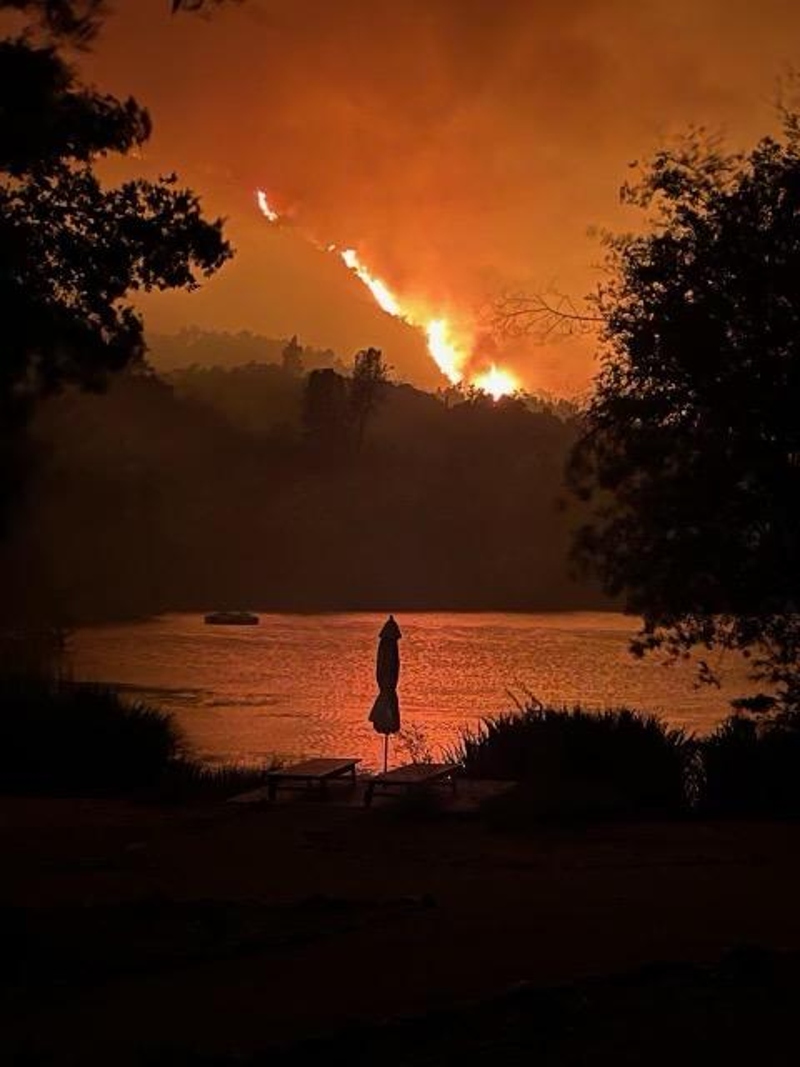
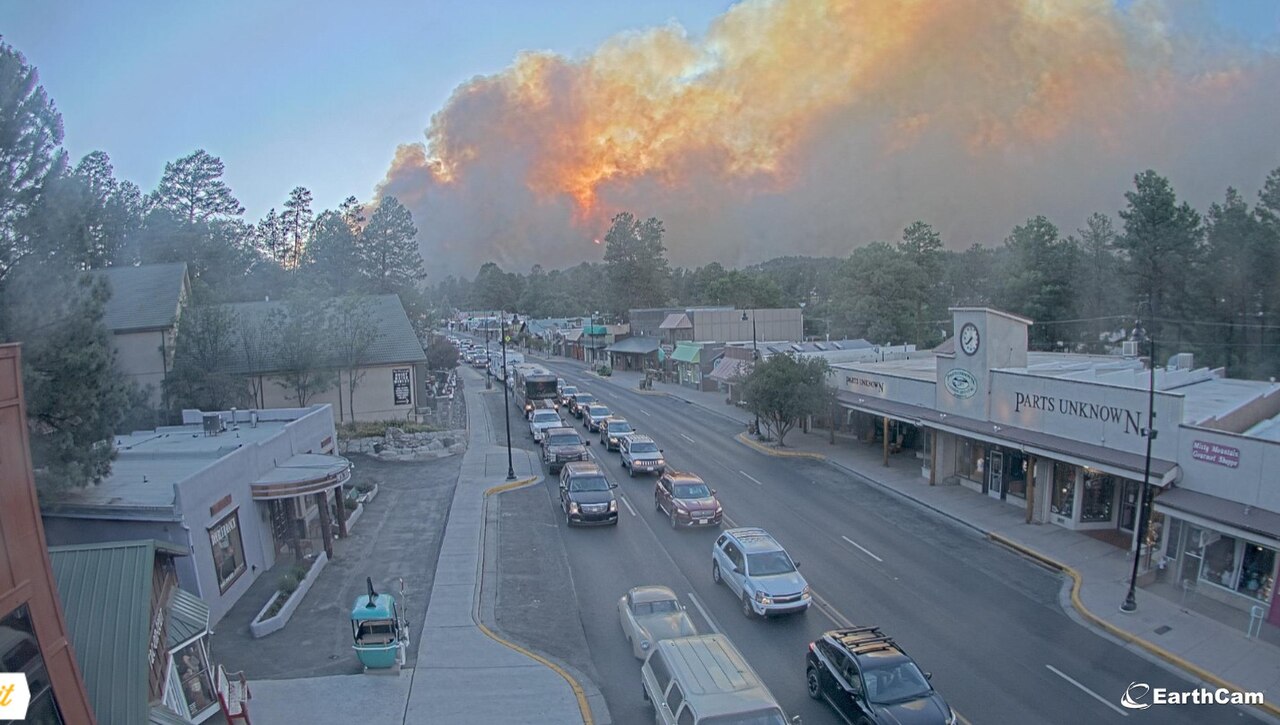
July 10, 2024 – Santa Barbara, CA – As California continues to battle the massive Lake Fire, scientists and meteorologists are observing a remarkable phenomenon: the fire is creating its own weather patterns. The Lake Fire, which began on July 5, 2024, in Santa Barbara County, has generated pyrocumulonimbus clouds, leading to unpredictable and dangerous conditions.
The Science Behind Fire-Induced Weather
When wildfires reach a certain intensity, they produce immense heat that forces air to rise rapidly. This rising air can cool and condense, forming clouds similar to those seen in thunderstorms. Known as pyrocumulonimbus clouds, these formations can produce strong winds, lightning, and even fire tornadoes. Such clouds have been observed forming over the Lake Fire, complicating firefighting efforts and creating hazardous conditions.
Current Fire Activity
Tactical firing operations continue ahead of the fire to control its spread. Significant activity on the southeast side of the fire footprint has prompted additional evacuations and an increase in acreage. Since the start of the Lake Fire, 1,500 people have been evacuated. There have been some firefighter injuries, though none were life-threatening, and medical responses have been quick and effective. An excessive heat warning remains in effect in the fire area.
Fuels and Weather Conditions
Precipitation and temperature alignments throughout the winter and spring of 2024 have resulted in an above-average load of herbaceous fuels. This creates a continuous fuel bed, allowing for rapid spread of fires when these fuels are dry. The current Red Flag Warning, with strong winds and hot, dry conditions, is expected to lead to increased fire growth.
Evacuations and Safety Measures
Authorities are urging residents in fire-prone areas to remain vigilant and heed evacuation orders promptly. Evacuation orders have been issued for parts of the Figueroa Mountain area, and warnings are in place for several other regions. Road closures and area closures are also in effect. Public safety is a top priority, and significant firefighting resources are deployed, including hand crews, engines, dozers, and air resources for water and retardant drops.
Looking Forward
As climate change continues to alter weather patterns, the frequency and intensity of wildfires in California are expected to increase. Understanding and adapting to the new challenges posed by fire-induced weather will be crucial in mitigating their impact. Researchers are actively studying these phenomena to develop better predictive models and firefighting strategies, hoping to stay one step ahead of the ever-evolving threats.
For more information on the Lake Fire, visit the Cal Fire incident page.